2020: COVID-19 Pandemic Declaration
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 virus epidemic a pandemic. This declaration marked a significant turning point in the global response to the pandemic, as it acknowledged the rapid spread of the virus worldwide and prompted countries to take more stringent measures to contain the outbreak.
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, is a contagious disease that has affected millions worldwide. Here are some key details about the virus:

Transmission and Symptoms
COVID-19 spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, vomiting, and loss of taste or smell. Some people may not show any symptoms at all.
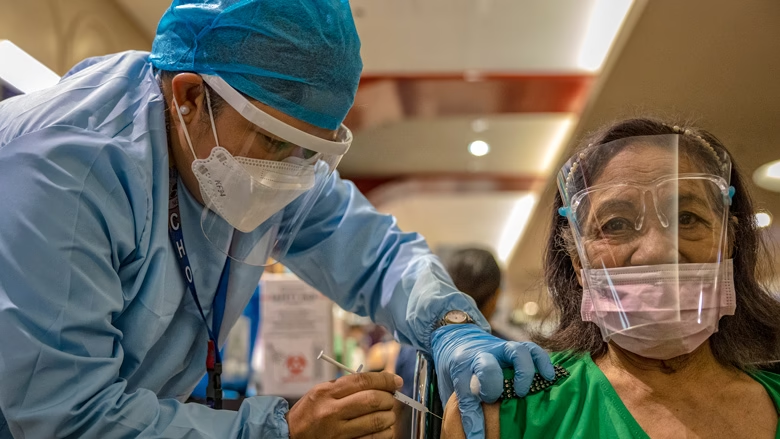
Prevention and Treatment
Preventive measures include getting vaccinated, wearing masks, maintaining social distancing, washing hands frequently, and avoiding crowded areas. Treatment for COVID-19 is primarily symptomatic and supportive, focusing on relieving symptoms and supporting the body’s immune response.

Vulnerable Groups
Certain groups are more susceptible to severe illness, including older adults, young children, and people with underlying health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and lung disease.
Long-term Effects
Some people may experience long-term effects, known as long COVID, which can include fatigue, muscle pain, and cognitive difficulties. The severity and duration of these effects vary widely.

Global Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on global health, economies, and societies. It has led to widespread lockdowns, travel restrictions, and a significant increase in remote work arrangements.